A Journey Through Time: The History of Uttar Pradesh
Nestled in the heart of India, Uttar Pradesh, often abbreviated as UP, is a state rich in history and culture. Stretching over 243,290 square kilometers, it is the most populous state in India, with a captivating history that dates back thousands of years. In this journey through time, we will explore the key epochs and events that have shaped the history of Uttar Pradesh.
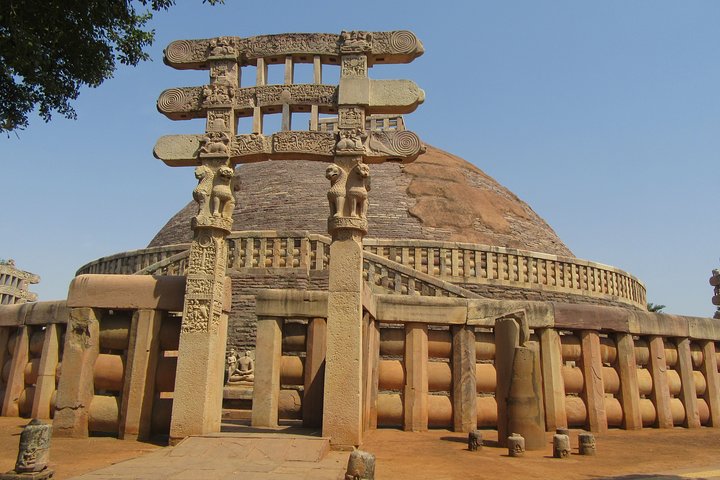

Ancient Uttar Pradesh (circa 2000 BCE - 600 CE)

The Vedic Era
Uttar Pradesh’s history can be traced back to the Vedic period, around 2000 BCE. The region was a major center for Vedic literature and learning. It is believed that many of the ancient Hindu scriptures, including the Rigveda, were composed in this fertile land along the banks of the Ganges River.
Mauryan Empire and Buddhism
During the reign of Emperor Ashoka (circa 268-232 BCE), Uttar Pradesh was an integral part of the Mauryan Empire. It was here that Buddhism began to flourish, with Sarnath serving as the place of Buddha’s first sermon. The city of Kaushambi also played a significant role in spreading Buddhist teachings.
Medieval Uttar Pradesh (circa 600 CE - 1526 CE)
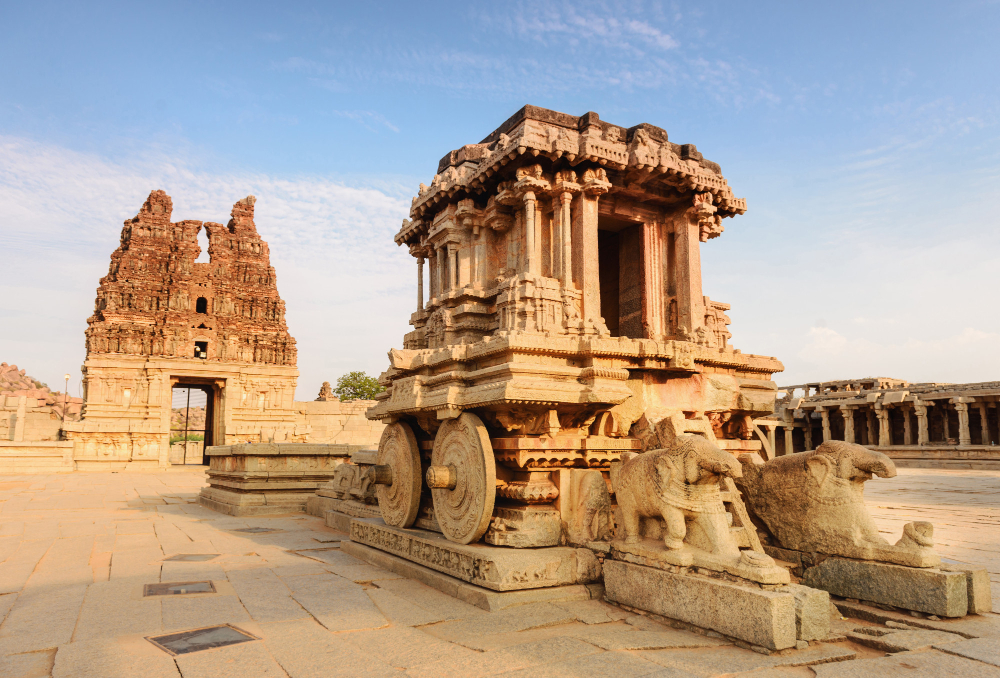

Gupta Empire
The Gupta Dynasty, which ruled from UP’s heartland, is often considered the golden age of Indian history. This era witnessed remarkable achievements in the fields of mathematics, art, and literature. The famous mathematician Aryabhata hailed from this region.
Delhi Sultanate and Mughal Empire
Uttar Pradesh became a crucial part of the Delhi Sultanate, followed by the Mughal Empire. Agra, in particular, emerged as a prominent center of Mughal power. The world-renowned Taj Mahal was built by Emperor Shah Jahan in Agra as a symbol of love and architectural excellence.
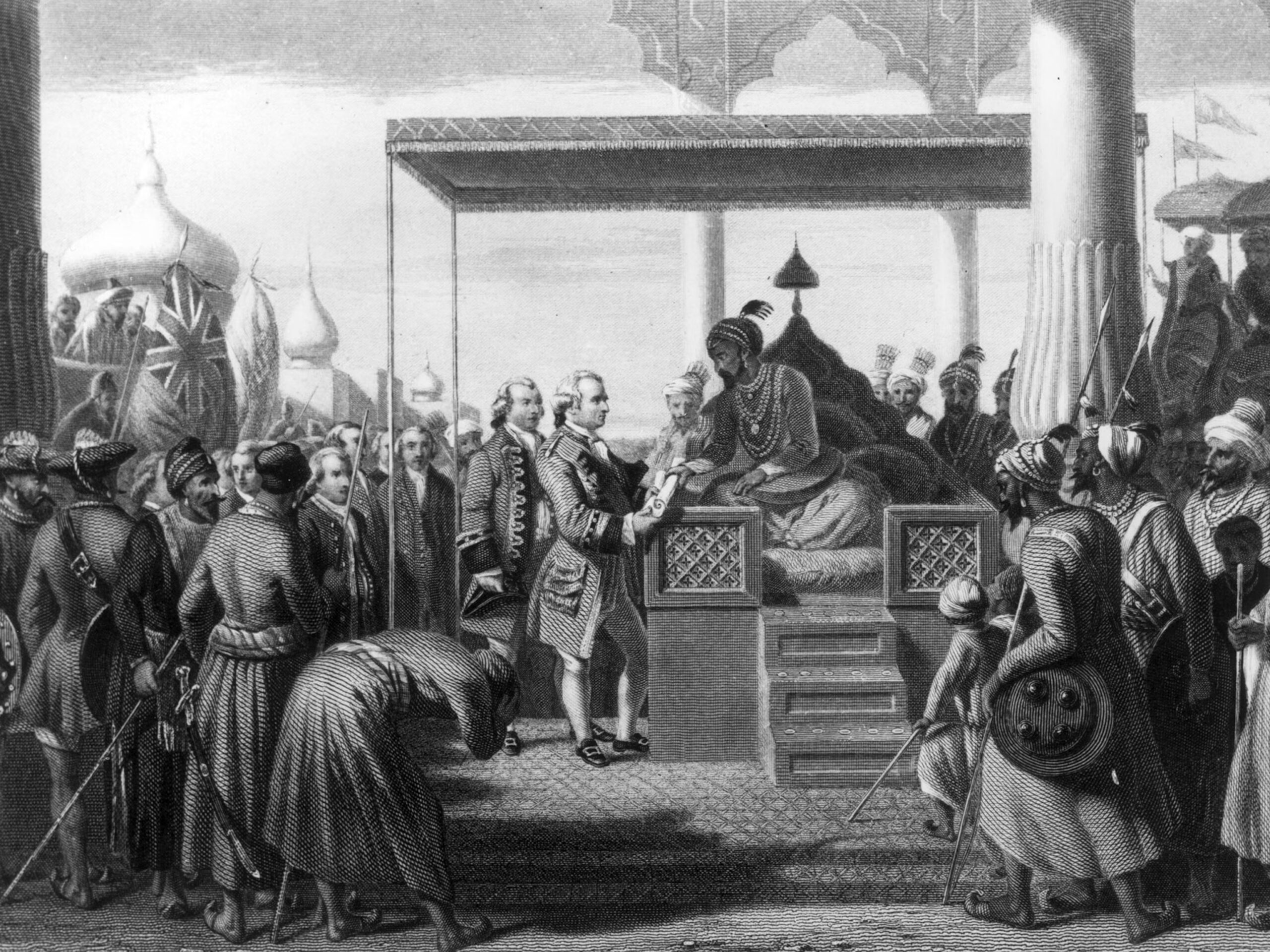


Colonial Era and Struggle for Independence
(circa 1757 CE - 1947 CE)

British Colonial Rule
The British East India Company established its foothold in Uttar Pradesh after the Battle of Buxar in 1764. The state played a pivotal role in the Indian Rebellion of 1857, also known as the First War of Independence. The uprising started in Meerut and rapidly spread across the region.
Leaders of Freedom Struggle
Uttar Pradesh was home to numerous freedom fighters, including Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri, and Sardar Patel. The state played a central role in the struggle for independence, with leaders like Mahatma Gandhi organizing various movements and protests.
Modern Uttar Pradesh (Post-Independence)
Formation of the State
On January 26, 1950, Uttar Pradesh officially became a part of the Republic of India. Lucknow was chosen as its capital, and the state has since grown into a vibrant and diverse region.
Socioeconomic Progress
In recent decades, Uttar Pradesh has made significant strides in various sectors, including agriculture, education, and industry. The state’s large population and fertile lands contribute significantly to India’s economy.

Cultural Diversity and Heritage
- Uttar Pradesh is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and traditions.
- The state is renowned for its classical arts, including Kathak dance and Hindustani classical music.
- The Kumbh Mela, one of the largest religious gatherings in the world, is held in Prayagraj (formerly Allahabad) and draws millions of pilgrims.
Tourism and Landmarks
- Uttar Pradesh boasts a plethora of historical and architectural marvels.
- Agra's Taj Mahal, Fatehpur Sikri, and the Agra Fort are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- Varanasi, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, holds spiritual significance for Hindus.
- Varanasi is famous for its ghats along the Ganges River.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Uttar Pradesh has seen remarkable progress but faces various challenges.
- Challenges include poverty, infrastructure development, and social issues.
- The state, with its vast resources and dynamic population, has the potential to overcome these hurdles and continue its journey towards prosperity.
REFER
A FRIEND
MEMBERS
BENEFITS
BECOME
A MEMBER
Our Sponsors







